Lesions classified as Cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD) largely encompass three different sub-groups: Florid, focal and periapical lesions. Presentation is said. Cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD) is a benign condition of the jaws that may arise from the fibroblasts of the periodontal ligaments. It is most common in. Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD) is a very rare benign lesion arising from a group of disorders which are known to originate from undifferentiated.
| Author: | Zulkikus Maramar |
| Country: | South Sudan |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Relationship |
| Published (Last): | 8 October 2024 |
| Pages: | 461 |
| PDF File Size: | 14.16 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 11.24 Mb |
| ISBN: | 466-4-28608-111-4 |
| Downloads: | 95236 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Zuluzshura |
Observations of similar asymptomatic radiopaque lesions over a long period enable us to predict their behaviour and ensure there are no negative changes of the lesion except what appears to be normal progression from radiolucency to radio-opacity.
Cemento-osseous dysplasia of the jaws in 54 Japanese patients: The mobility of teeth, the severe periodontitis, the persistence of signs of inflammation, and the slight pain reported by the patient, lead us to extract the three teeth involved; the subsequent persistence of swelling then indicated a biopsy should be taken, and this established the diagnosis. A clinical and histopathologic study of fifteen cases.
Cemento-osseous dysplasia
Cysts and cystic lesions of the mandible: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology3rd Edition. Histological examination revealed multiple small fragments of cementum-like substances characterized by islands of calcified deposits and areas of loose fibrocollagenous stroma Figure 3 ; the latter showed evidence of proliferation.
Dysplaska rare manifestation in an Indian family. There is no treatment necessary for any type of COD. A clinical-pathologic study of thirty-four cases.
The clinicopathologic spectrum of cementoosseous dysplasia. None, Conflict of Interest: Clinical and Radiographic Analysis Share on.
Cemento-osseous dysplasia - Wikipedia
dys;lasia The lesions differ in their clinical manifestations and biological behavior, and should, thus, be managed by different approaches. Post-extraction healing was particularly slow, with slight but persistent swelling, limited to the area around These similarities make it difficult to definitively diagnose the condition on the basis of microscopic features alone.
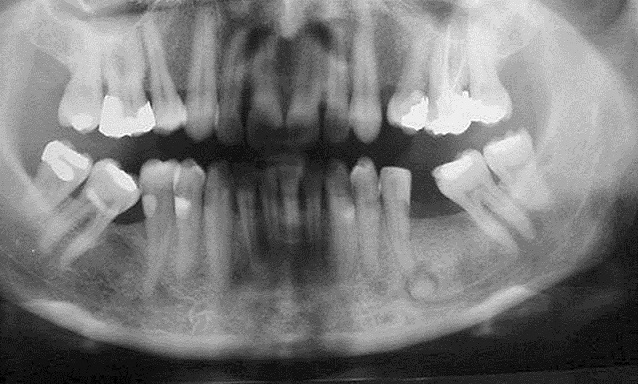
Radiographically, the lesions appear as multiple sclerotic masses in the tooth-bearing regions which usually affect the mandible on both sides in a symmetrical manner, but all four quadrants may be involved, it presents as multiple radiopaque lesions that fuse into lobulated sclerotic masses.
In this case report an FCOD is presented, which is located between the first premolar and the second molar on the left side mandible of a year-old female patient. Abstract Introduction Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia is one of the terms that have been designated by the World Health Organization as cemento-osseous dysplasias of the jaws.
Epub Jan Previous Section Next Section. Univariate analysis of the data involved descriptive statistics i. Extractions of the mandibular left third molar and the maxillary left first molar were done in and respectively under antibiotic coverage of Amoxicillin mg three times daily for 5 days for periodontal reasons and without any difficulty or complications.
Case report A case of asymptomatic uncomplicated florid cemento-osseous dysplasia occurring in a year-old Jordanian female is reported, which can be considered rare regarding race distribution.
The majority of patients in the current study The definitive diagnosis for this case was periapical COD. Basic Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.
A clinical-pathologic study of thirty-four cases. According to the classification system introduced by the Revised World Health Organization WHO Guidelines, Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia is categorized as a form of neoplasm or other bone-related lesion; it can be sub-divided into periapical cemental dysplasia PCDalso known as periapical fibrous dysplasia, florid COD also known as gigantiform cementoma or familial multiple cementoma and other types of COD 23.
Expansive focal cemento-osseous dysplasia. Clinical, radiographic, biochemical and histological findings of florid cemento-osseous dysplasia and report of a case. Florid COD is characterized by multifocal involvement of the jaw. A year-old Jordanian female patient attended the periodontal clinic at King Hussein Medical Centre in for periodontal assessment.
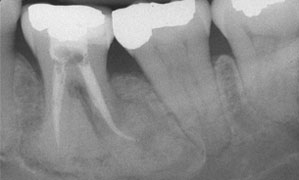
Minor radiolucency could be recognized around the roots while the high dense deposit within the bone is obvious at the mandibular associated lesions. Intraoral examination showed that the maxilla was completely edentulous; the mandible contained only six teeth: This evolution may take months or years, and during its development, the diameter of the lesion increases from 0.
Biopsy specimens were sent to the Department of Oral Pathology, where sections were cut and prepared conventionally, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. This Article Anticancer Research May vol. Lam is associate professor and head, discipline of oral and maxillofacial radiology, faculty of dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario. Endoral radiography showed that these teeth had been devitalized; they had deep periodontal pockets and marked radicular radiotransparency; the root apices exhibited mixed radiotransparency and radio-opacity.
For all but 3 of the patients, clinical features had been recorded.
Osseous (Cemento-osseous) Dysplasia of the Jaws: Clinical and Radiographic Analysis | jcda
Report of four cases. Competing interests None declared. Ossifying fibroma-cementoma of jaw. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. The lesion caused perforation and expansion of alveolar bone. In some cases, the radiographic image can be misinterpreted as an infection of endodontic origin, and thus mismanaged Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours.
A complete or partial radiolucent dyslpasia was noted in a few reports 12,13,22 and a sclerotic border has been less frequently reported 2,14,22 Fig. None of her family reported to have similar conditions. Clinical, radiographic, and histological findings of florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: Of the patients for whom age and sex were known, the majority 97 [ In this retrospective analysis, COD more usually occurs in the mandible, both in tooth-bearing and edentulous areas, but may occasionally occur in the maxilla.
