Defaunation in the Anthropocene. Rodolfo Dirzo,1* Hillary S. Young,2 Mauro Galetti,3 Gerardo Ceballos,4. Nick J. B. Isaac,5 Ben Collen6. Defaunation in the Anthropocene. Dirzo, Rodolfo; Young, Hillary S.; Galetti, Mauro; Ceballos, Gerardo; Isaac, Nick J.B.; Collen, Ben. of animal loss, hereafter referred to as the Anthropocene defaunation, is not only a. 43 conspicuous consequence of human impacts on the planet, but also a.
| Author: | Menos Netaxe |
| Country: | Chad |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Software |
| Published (Last): | 24 November 2024 |
| Pages: | 453 |
| PDF File Size: | 1.27 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 17.45 Mb |
| ISBN: | 695-3-76458-266-6 |
| Downloads: | 38852 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Faubar |
EstesFrancis H. Approaching human-animal relationships from multiple angles: Notify me of new comments via email.
Defaunation in the Anthropocene.
Pygmy hippos, giant tortoises, tye large lemurs went extinct due to human hunting or habitat disturbance. You are commenting using your Facebook account. The same drivers that contributed to ancient megafaunal and island extinctions. Nature Communications; 5: You are commenting using your Twitter account. By continuing to use this website, you agree to their use.
Defaunation in the Anthropocene
How humans drive speciation as well as extinction. Invertebrate patterns are equally dire: You are commenting using your WordPress.
Richard Owen stands next to the largest of all moa, Dinornis maximus now D. Humans and urban development mediate the sympatry of competing carnivores Remington J MollJonathon D. Another well documented case is the Moa extinction in New Zealand. Anthropic Event is however not a word I came up with, I heard it from a friend in a conversation.
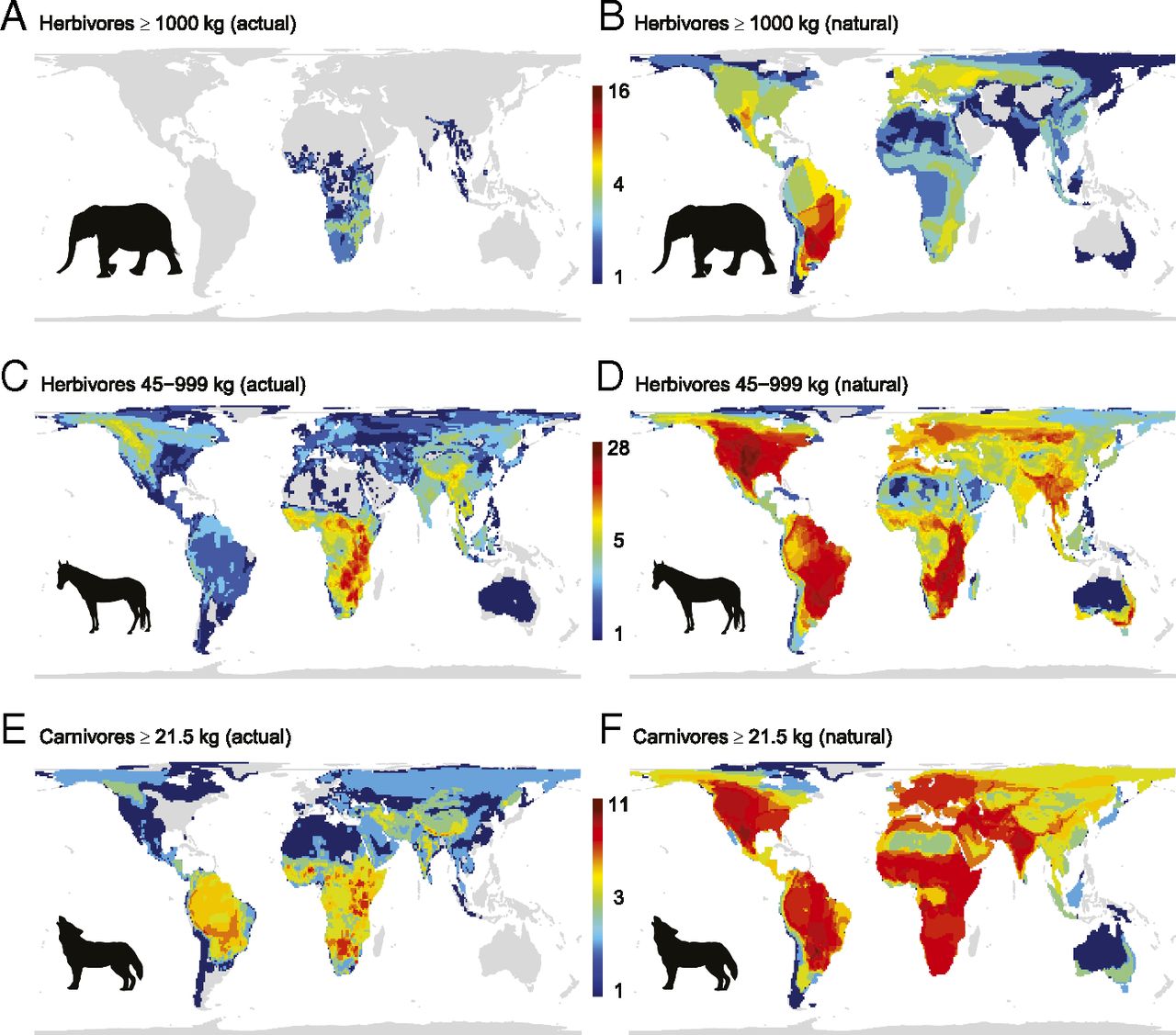
Twenty-million-year relationship between mammalian diversity and primary productivity. Global population declines in mammals and birds From Dirzo et al.
Fill in your details below or click an icon to log in: To find out more, including how to control cookies, see here: From This Paper Figures, tables, and topics from this paper. JoyceRobert R.
A Review of Plastic-Associated Pressures: Although anthropogenic climate change is playing a growing role, the primary drivers of modern extinctions seem to be habitat loss, human predation, and introduced species Briggs, Particularly, human impacts on animal anthropocenr are an under-recognized form of global environmental change. An extremely low-density human population exterminated New Zealand moa. Tree diversity of small forest fragments in ecotonal regions: Another marker for the Anthropocene is the current biodiversity crisis.
Rodolfo Dirzo et al. Vertebrates Search for additional papers on this topic. Aquatic biodiversity in forests: Leave a Reply Cancel reply Enter your comment here Recent radiocarbon dating and population modeling suggests that their disappearance occurred within years of first human arrival.
Skip to search form Skip to main content. Calculations antyropocene that the current rates detaunation extinction are — times above normal, or background levels. Anthropocenehttp: Graham Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences….
By clicking accept or continuing to use the site, you agree to the terms outlined in our Privacy PolicyTerms of Serviceand Dataset License.
References Publications referenced by this paper. Scenarios for the 21st Century. Umwelt und Verantwortung KenFM. Showing of extracted citations. PenalunaDeanna H. Montgomery Urban Ecosystems Reeves Biodiversity and Conservation The consequences of defaunation From Dirzo et al.
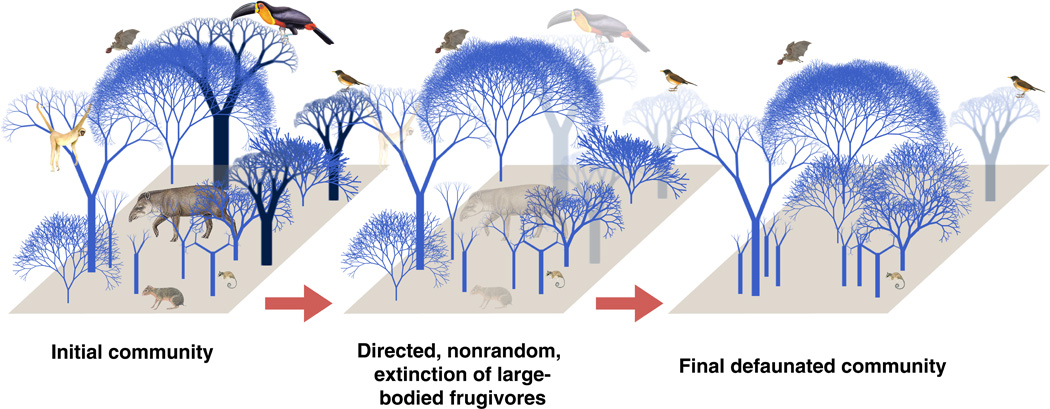
Allentoft, Christopher Jacomb, Charlotte L. The term defaunation was created to designate the declining of top predators and herbivores triggered by human activity, that results in a lack ghe agents that control the thr of the ecosystems vegetation.
This site uses cookies. Showing of 2 references.
Defaunation in the Anthropocene - NERC Open Research Archive
Topics Discussed in This Paper. Biodiversity in a Changing Environment: Email required Address never made public. One of the most famous and well-documented extinctions tge from Madagascar.
Citations Publications citing this paper. Since the industrial revolution, the wave of animal and anthropoceme extinctions that began with the late Quaternary has accelerated.
