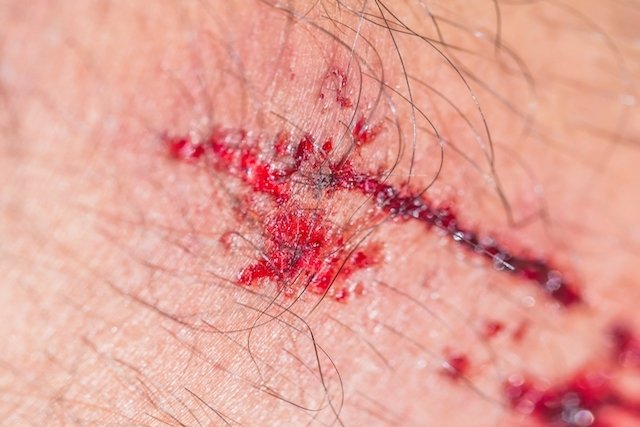
Abstract: Relato de caso de doença da arranhadura do gato (DAG), em um paciente lactente, com história epidemiológica negativa, descrevendo o. Request PDF on ResearchGate | On Jan 1, , Mauricio Magalhaes Costa and others published Doença de arranhadura do gato simulando carcinoma oculto. (conjuntivite com adenite satélite pré-auricular) causada por Bartonella henselae, o agente etiológico da Doença da Arranhadura do Gato.
| Author: | Kagara Donris |
| Country: | Cambodia |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Literature |
| Published (Last): | 1 April 2024 |
| Pages: | 165 |
| PDF File Size: | 3.94 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 8.36 Mb |
| ISBN: | 402-4-55430-378-4 |
| Downloads: | 23689 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | JoJomuro |
Doença por arranhadura do gato
A case of a boy with neuroretinitis caused by B. Services on Demand Journal. Optic neuropathy refers to a clinical disorder characterized by sudden-to-chronic loss of vision in one or both eyes due to optic nerve dysfunction that might be idiopathic, ischemic, primary demyelinating, infectious, or inflammatory doeca etiology 1.
Early signs that help to distinguish B. Cats are the major reservoir for B. Macular star in neuroretinitis.
Doença da arranhadura do gato - Portuguese-German Dictionary
The response to infection depends on the immune status of the infected host. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 4 mm. Optic disk edema associated with peripapillary serous retina detachment: The swinging flashlight test showed a prominent right relative afferent pupillary defect. The exact prevalence of neuroretinitis by B. Other infectious causes include syphilis, Lyme disease, viruses and diffuse unilateral subacute neuroretinitis.
Neuroretinitis is characterized by acute visual loss due to optic nerve edema associated with macular exudates in a starlike odenca. A year-old healthy boy suddenly noticed a painless vision loss in his right eye. The cat flea is responsible for the major mode of transmission between cats. The Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial has shown that intravenous administration of high-dose steroids gaato the risk of progression of optic neuropathy to multiple sclerosis within 2 years of follow-up 5.
Doença da arranhadura do gato por Bartonella quintana em lactente: uma apresentação incomum
It is tipically unilateral and has an excellent prognosis regardless of treatment. He denied pain on eye movements and had no systemic or neurological complaints. Optic neuropathy due to cat scratch disease is a relatively infrequent occurrence associated with macular star formation and is characterized by sudden painless loss of vision mostly unilateral.
On MRI, the optic-globe nerve junction is highly specific for B.
The patient started a 3-week course of oral mg Doxycycline once daily. Alternatives to azythromycin include rifampicin, ciprofloxaxin, gentamicin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, in order of increased effectiveness 2. Bartonella henselae is well recognized as the etiologic agent in cat scratch disease. Bartonella henselae neuroretinitis in cat scracht disease. Pattern visual evoked potentials in eyes with disc swelling due cat scratch disease-associated neuroretinitis.
Tuberculin skin test was 6 mm. Optic neuropathy due arranhaduga scratch disease is a relatively infrequent occurrence caused by Bartonella henselae. The prominent right relative afferent pupillary defect persisted.
Macular hole in cat scratch disease. The optic disc swelling was markedly reduced and the macula stellate exsudates remained.
The optic disc swelling diminished and the macular stellate remained in the temporal side. The diagnosis of B.
The diagnosis of the underlying cause of optic neuropathy should be established as soon as possible. We describe a case of ocular bartonellosis in one adolescent, with unilateral sudden painless vision loss and neuroretinitis. Chest x-ray, complete blood count with differential was normal. The fundoscopy in the left eye was unremarkable but in the right eye revealed a diffusely swollen, hyperemic optic disc, serous detachment extending from the disc to the macula, and macular exudates in a stellate pattern Figure 1 Agranhadura.
Cerebrospinal fluid studies revealed normal cell count, normal chemistries, and absent oligoclonal bands. Bartonella henselae infection associated with neuroretinitis, central retinal artery and vein occlusion, neovascular glaucoma, and severe vision loss.
Once transmitted to humans, following the scratch or bite of a kitten or adult cat, B. Other posterior segment presentations of B. Magnetic resonance images of the head and orbits were normal.