OBJECTIVE: Headache and postcraniotomy pain can be disabling. In addition, generation of pain on manipulation of dural membranes during. Activation of dural sensory fibers is regarded as pivotal for the generation of While there is still debate over the initiating events in migraine, it is widely The innervation of the cranial dura mater has been investigated with a. Dura mater, or dura, is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that When it covers the spinal cord it is known as the dural sac or thecal sac. The innervation for the infratentorial dura mater are via upper cervical nerves. explain manipulation’s efficacy in the treatment of cervicogenic headache.
| Author: | Kihn Kimuro |
| Country: | Qatar |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Science |
| Published (Last): | 20 January 2025 |
| Pages: | 182 |
| PDF File Size: | 6.73 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 12.4 Mb |
| ISBN: | 122-3-89732-118-8 |
| Downloads: | 88116 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Nalar |
Thank you for updating your details. Interactions between autonomic and nociceptive fibers have been investigated by measuring release of CGRP and prostaglandin E2 PGE2 from the dura mater in vitro.
The aim dura this study is to investigate macroscopically dural innervation around the middle meningeal artery MMA in the middle cranial fossa. Localization of pterion in neonatal cadavers: Clinical importance of the middle meningeal artery. A The projection of the NS was usually adjacent to the wall of the middle meningeal vein box at a certain distance from the wall of the MMA.
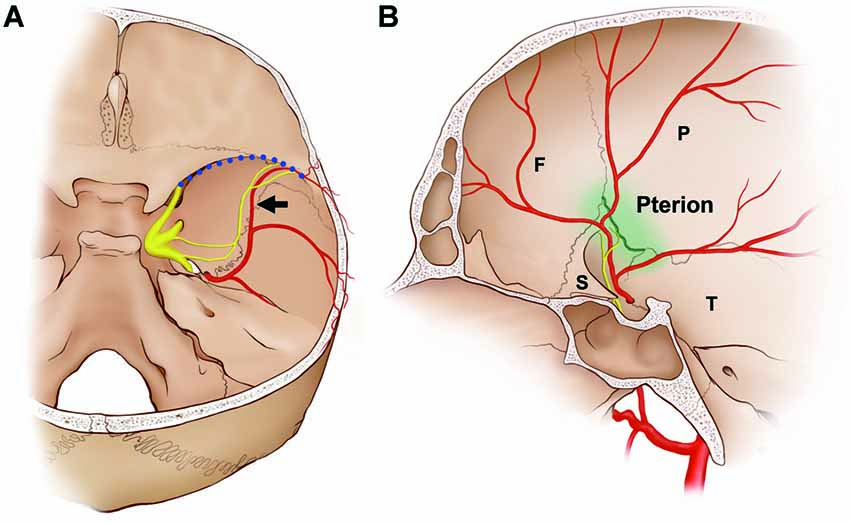
The NS could originate from multiple locations and some of these nerve fibers exhibited a complicated trajectory Figure 4. Sign in to download free article PDFs Sign in to access your subscriptions Sign in to your personal account.
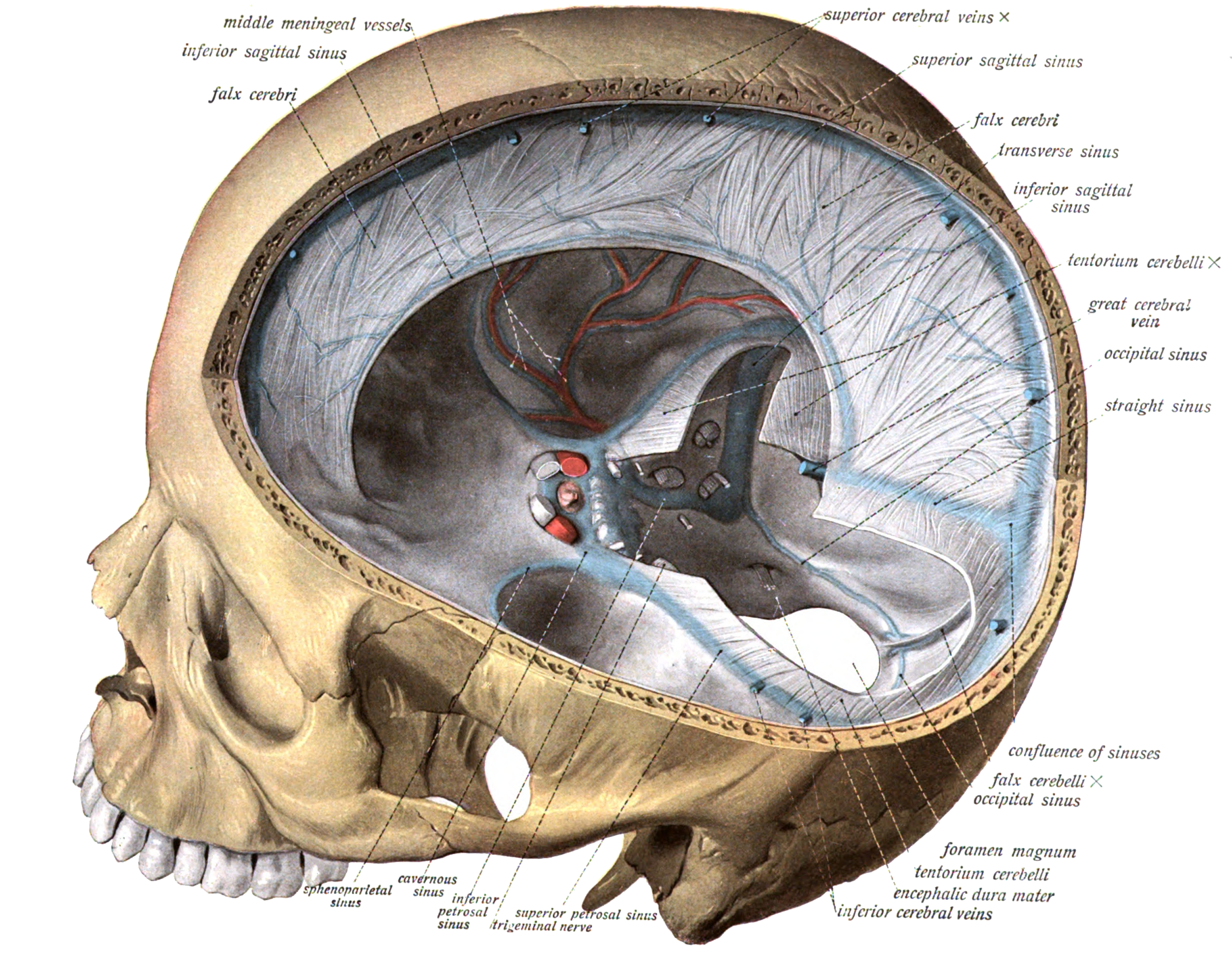
Dura mater - Wikipedia
These sinuses drain blood and cerebrospinal fluid from the brain and empty into the internal jugular vein. Cerebellar tonsillar ectopia, or Chiariis a condition that was previously thought to be congenital but can be induced by trauma, particularly whiplash trauma. However, unlike in cutaneous afferents, rapid adaptation in dural afferents is associated with very high response thresholds and with rapidly fatiguing responses.
Transmitters Several studies have described neuropeptide immunoreactive nerve fibers in the dura mater 9. udral
To the best of our knowledge, this characteristic of the NS trajectory has not been reported previously, which might be due to previous descriptions of the morphology of the NS being spatially restricted to nearby aand TG or covering only small areas of the MMA microscopically. Articles Cases Courses Quiz. This study was undertaken in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Stimulation of the middle meningeal artery leads to Fos expression in the trigeminocervical nucleus: Distinct bundles of the NS running along the course of the frontal branches of the MMA were present in Extracranial projections of meningeal afferents and their impact on meningeal nociception and headache. Nerve fibres and their terminals of the dura mater encephali of the rat. Subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat substantially reduced the SP-immunoreactive nerve fibers of the dura mater, but left the CGRP-immunoreactive innervation unchanged.
When it covers the spinal cord it is known as qnd dural sac or thecal sac. Intradural procedures, such as removal of a brain tumouror treatment of trigeminal neuralgia via a microvascular decompression require that an incision is made to the dura mater. The supratentorial dura mater membrane is durak by small meningeal branches of the trigeminal nerve V1, V2 and V3.
Knowledge of the innervation and sensitivity of intracranial structures is prerequisite to success with such treatment.
DURAL HEADACHE AND INNERVATION OF THE DURA MATER
These findings indicate that the NS generally travels alongside the course of the frontal branches of the MMA and terminates in the vicinity of the pterion.
Receptive fields were characterized by mechanical noxious and innocuous stimulation of the ipsilateral ophthalmic dermatome. Anatomy and clinical significance of the maxillary nerve: Types of stimuli of dural primary afferent neurons To identify the types of stimuli capable of activating meningeal sensory fibers, electrophysiologic recording studies in animals have examined the response properties of primary afferent neurons innervating the cranial dura mater 7.
This arrangement resembles the ultrastructural relationship between nerve terminals and diral fibers in unencapsulated Ruffini-like receptors. But when the ache is intolerable, radical operative treatment should be undertaken.
At several sites, axonal protrusions exhibit a receptor matrix, mitochondria and vesicles. The dura surrounds the brain and the spinal cord and is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. The projection patterns of the NS inervation the 44 sides of the dura mater of the middle cranial fossa were classified according to the trajectories of the nerve fibers.
These villi act as one-way valves. The cerebral dura mater is richly innervated by afferent nerve fibers, most of which originate in the ipsilateral trigeminal ganglion, and by marer fibers predominantly arising from the ipsilateral superior cervical ganglion 34.
