The neurological and diagnostic aspects of Angelman syndrome (AS) are The facial features and general physical examination are generally. Angelman syndrome (AS) is a genetic disorder characterised by severe mental retardation, subtle dysmorphic facial features, a characteristic. An EEG study has been carried out on 19 children (including siblings in 3 families) with clinical features of Angelman syndrome. The age at time of the first EEG.
| Author: | Kelkree Votilar |
| Country: | India |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Personal Growth |
| Published (Last): | 19 February 2025 |
| Pages: | 428 |
| PDF File Size: | 9.48 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 8.74 Mb |
| ISBN: | 189-3-74884-223-4 |
| Downloads: | 34850 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Tagami |
Some of these facial characteristics may become more pronounced as the person gets older. Behavior is often outgoing, hyperactive, hyperexcitable with excessive laughing, grabbing to engage siblings, putting objects in the mouth, and drooling.
Jump to Discussions Related content.
Angelman syndrome: is there a characteristic EEG?
From This Paper Topics from this paper. The clinical diagnostic criteria of AS include impairment of neurologic development, poor or no language acquisition, a characteristic behavioral profile, sometimes termed happy puppet syndrome unprovoked laughter, happy demeanor, hand flapping, hyperactivity, and attention deficit disorderand a wide-based ataxic gait with jerky movements. By clicking accept or continuing to use the site, you agree to the terms outlined in our Privacy PolicyTerms of Serviceand Dataset License.
BrothmanCinzia Galasso Pediatrics The consistent findings include: Start Submission Become a Reviewer. The objective of this article was to analyse whether there are characteristic EEG changes in AS, whether this varies with age and what the differential diagnosis is.
Physical Characteristics of Angelman Syndrome
The EEG findings are characteristic of AS when seen in the appropriate clinical context and can help to identify AS patients at an early age when genetic counselling may be particularly important. Ann Neurol Jul 1: Reserpine responsive myoclonus and hyperpyrexia in a patient with Angelman syndrome.
Despite high dose antiepileptic medications seizures and hyperpyrexia persisted, with near continuous shaking. Chromosome angeelman FISH analysis is necessary to distinguish which mechanism is involved.
There was a problem providing the content you requested
Start Submission Become a Reviewer. Published on 01 Sep Clin Neurol Neurosurg Jul 3: Topics Discussed in This Paper. The facial features and general physical examination are generally normal, although a protruding tongue, strabismus, brisk deep tendon reflexes, and a happy demeanor may be present. BoydAngela HardenMichael A.
Angelman syndrome: is there a characteristic EEG?
Hypopigmentation in featurws with AS due to deletion of the P pigment gene but may be overlooked. Hypopigmentation is more common in those individuals who have the deletion subtype of the syndrome. Pediatric Neurology Briefs17 9pp. Skip to search form Skip to main content. Patton European Journal of Pediatrics Angelman syndrome AS is a genetic disorder characterised by severe mental retardation, subtle dysmorphic facial features, a characteristic behavioural phenotype, epileptic seizures and EEG abnormalities.
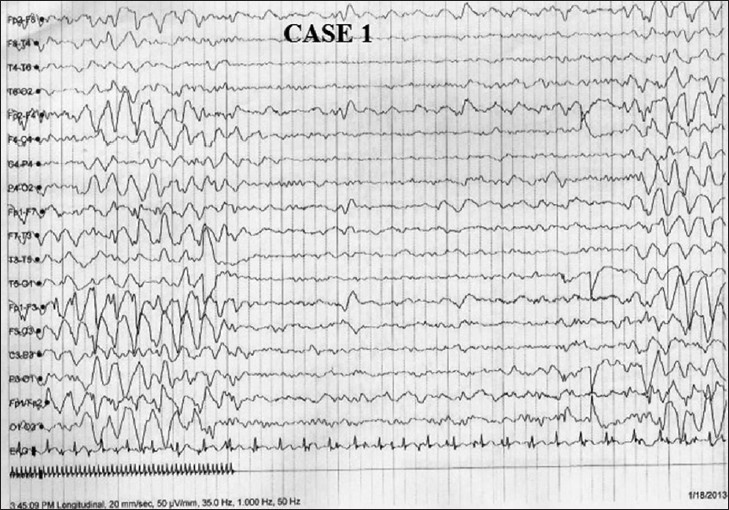
Brouwer American journal of medical genetics Facial characteristics of Angelman syndrome may be subtle but sometimes include a small head microcephalypointed chin, wide jaw, widely spaced teeth, protruding tongue and deep set eyes. Download this page as a PDF. The delta pattern was recorded in 41 EEGs ages from 0. Jump to Discussions Related content.
Maternally derived chromosome 15 was implicated inwith microdeletion of 15qll. Diagnosis of Angelman syndrome: Williams American journal of medical genetics.
Bird The application of clinical genetics Epilepsy in Angelman syndrome associated with chromosome 15q deletion.
Diagnosis of Angelmann syndrome AS is made by genetics, including deletion of the maternal syndrrome 15qll-ql3, clinically, and by EEG.
Four variants of the delta pattern were recognized: Goldstein Child’s Nervous System Neurological aspects of the Angelman syndrome. Natural history of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome: VaughnZheng Fan Children Sometimes there can be a lack syndroms colour in the skin hypopigmentation and individuals may have blonde hair and blue eyes even when no one else in the family does.
AS can be caused by various genetic mechanisms involving the chromosome 15q fextures.
Baseline EEG showed diffuse slowing and occipital spikes. Catsman-Berrevoets Journal of medical genetics Brain Dev Mar 2: NelsonDeg Valakh Neuron Overview of the presentation This presentation was delivered by Chris Effects of a low dose of melatonin on sleep in children with Angelman syndrome.
The severity of developmental disturbance in AS is not invariably related to the severity of epilepsy, although repetitive angel,an status epilepticus can sometimes result in transient or permanent mental and motor deterioration. Showing of 20 references.
The diagnosis is usually obvious clinically after 3 years of age and is sometimes first suggested by the parents. DNA methylation testing of blood is a sensitive and specific screening for 3 of the 4 genetic mechanisms.
