It was established by the Gram Nyayalayas Act, Gram Nyayalayas are mobile village courts in India established for speedy and easy access to justice. (1) For the purpose of exercising the jurisdiction and powers conferred on a Gram Nyayalaya by this Act, the State Government, after consultation with the High. Keywords: nyaya panchayats, alternate disputes redessal, gram nyayalaya act. 1. Introduction. Some form of village self-government seems to have some form.

| Author: | Doujar Banris |
| Country: | Sweden |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Personal Growth |
| Published (Last): | 16 August 2024 |
| Pages: | 193 |
| PDF File Size: | 14.56 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 8.12 Mb |
| ISBN: | 916-7-58848-776-5 |
| Downloads: | 99946 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Kira |
The Gram Nyayalaya uneasily straddles two approaches to legal system reform: The Gram Nyayalaya shall try to settle the disputes as far nyajalaya possible by bringing about conciliation between the parties and for this purpose; it shall make use of the conciliators to be appointed for this purpose. It should be clear then that the Act does not impose the consensual resolution of disputes on parties; they may seek adversarial adjudication and engage lawyers to appear for them before the Gram Nyayalaya if an amicable resolution does not appear possible.
This was sought to be ensured by the presence of lay-judges and a mobile court, but also rather amorphously by the reduced application of procedural law. The Act mandated setting up of 5, ac courts till Therefore, it was decided that gram nyayalayas would have jurisdiction over more than one panchayat. Both these approaches rest on an understanding of a legal system which are conceptually inadequate and empirically suspect.
Each Gram Nyayalaya exercises the power of a Civil Court with some modification such as special procedure as mentioned in the act. Power of State Government to make rules. Salary, allowances and other terms and conditions of service of Nyayadhikari. That is how the Centre decided to set up 5, gram nyayalayas. Creation of a regular cadre of Gram Nyayadhikari: One of the objectives was also to atc pendency in courts and to improve India’s dismal judge-to-population ratio.
Yet to become operational Haryana Proposed setting up of 2 Gram Nyayalayas. The Act has added the lowest tier of courts of subordinate judiciary in addition to the regular civil and criminal courts. Comments Based on Notes on Clauses of the Bill. The Preamble to the Gram Nyayalaya Act envisages access to justice to the citizens at their doorstep with the assurance that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of any disability whatsoever. Andhra Pradesh Proposal for setting up of Gram Nyayalayas pending.
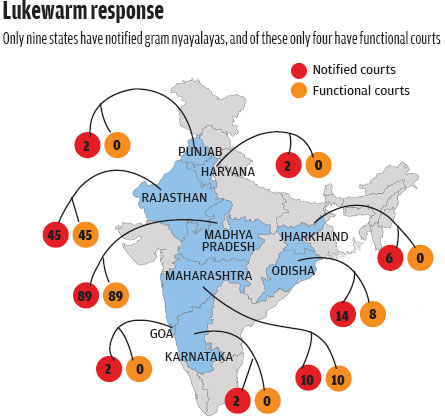
West Bengal Proposed to seek full financial assistance for implementation of the Act. Headquarters of Gram Nyayalaya. The number of cases disposed by Gram Nyayalayas is negligible and that they do not make any substantial difference in the overall pendency nyayalsya the subordinate courts.
Subscribe to Weekly Newsletter:.
It had also estimated that the states would have to bear a recurring cost of Rs 6. The Gram Nyayalaya Act was passed in to make the judicial process participatory, inexpensive and accessible to rural India.
District Courts of India List grqm district courts of India. The Act was enacted “to provide for the establishment of the Gram Nyayalayas at the grass root level for the purpose of providing access to justice to the citizens at their door steps and to ensure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of social, economic nyagalaya other disabilities Over the years successive Governments have tried in their own ways to strengthen the judicial system.
There has been no rigorous assessment of the justice enhancing properties of these nayalaya strategies. Where are rural courts? Civil and Property suits such as use of common pasture, water channels, farms, right to draw water from a well or tube well etc. Some government sources, who do not wish to be identified, also shared alarming information with us on the states’ apathy towards making justice accessible to all.
Nyayadhikari not to preside over proceedings in which he is interested. Till Decembermillion cases were pending in courts across India. Provided that nothing in this sub-section shall preclude any person from availing of the judicial remedies available under articles 32 and of the Constitution. Establishment of Gram Nyayalayas.
Gram Nyayalayas
The tribal areas in Mizoram and Nagaland have been exempted and garm non-tribal areas, these North Eastern states have expressed their willingness to set up Gram Nyayalayas subject to elimination of certain legal impediments, not specified. Procedure in Criminal Cases. Free for one month and pay only if you like it. Special procedure in civil disputes. Creation of a regular cadre of Gram Nyayadhikari: A legal procedure used for enforcing a right that takes effect faster and more efficiently than ordinary methods.
The principles of equality and justice are realized by the State apparatus through the business of administration of justice. Besides, inadequate infrastructure, non-availability of judicial officers to function as Gram Nyayadhikaries and problem of concurrent jurisdiction of regular courts were also impeding the speedy operationalization of the scheme.
GRAM NYAYALAYAS | Common Cause
Implementation of the Act, which has been left to the states, has been dismal across the country. No notification as yet.
The way nyayalaa The Preamble to the Gram Nyayalaya Act envisages access to justice to the citizens at their doorstep with the assurance that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of any disability whatsoever.
Where states stand In a conference of chief ministers and chief justices of high courts held gtam Delhi on April 7 last year, the then chief minister of Gujarat, Narendra Modi, said the implementation of the Act was financially untenable and talked about how courts have been set up at the block level in Gujarat to make justice accessible to rural litigants.
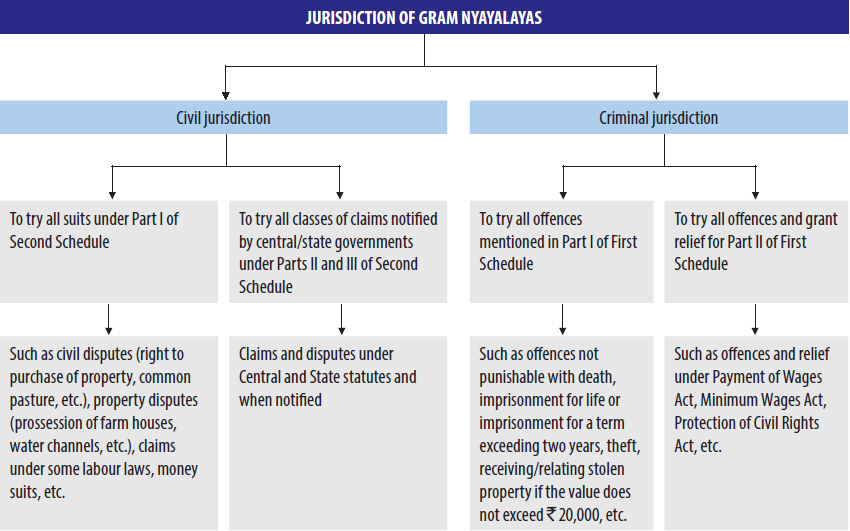
For example, there could be three gram nyayalayas in one block, with different numbers of panchayats under each nyayalaya. In terms of jurisdiction, the Law Commission was in favour of granting Gram Nyayalayas a relatively wide acct, roughly co-extensive with those of the Judicial Magistrate First Class and the Civil Judge Junior Division in criminal and civil cases respectively.
