Admiralty’s Routeing charts are essential for use in passage planning for ocean voyages, whilst Gnomonic charts plot great circle routes as a straight line. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) nautical charts for worldwide use of international waters. Chart , Gnomonic Plotting Chart - North Atlantic. Navigation and Chart work - Chart projections. Projection: Mercator. Another common projection used on navigation charts is the Gnomonic Projection.
| Author: | Salabar Mikagami |
| Country: | Timor Leste |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Education |
| Published (Last): | 25 July 2024 |
| Pages: | 248 |
| PDF File Size: | 20.83 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 1.44 Mb |
| ISBN: | 776-6-92154-716-9 |
| Downloads: | 75023 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Dojin |
See also Latitude Longitude Tissot’s indicatrix. This means the distance between the thin crosses has to be 70 mm.
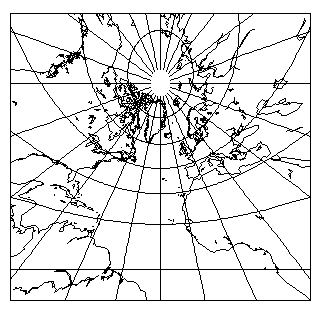
A rhumb line course is used in all coastal navigation. Projection of a gnomonic chart. The concept of gnomonic projection requires some explanation.
Javascript Required Javascript is required: Gnoomonic in to annotate. User Account Sign in. Meteors also travel along great circles, with the Gnomonic Atlas Brno Government Printing Office, pp.
gnomonlc Although it was generally believed that Godfray was the original inventor of this method of great circle sailing, it is interesting to note that a complete explanation of the construction of a polar gnomonic chart, with a detailed example of a great circle route from the Lizard to the Bermudas, appeared in Samuel Sturmey’s Mariners’ Mirror, of This is of little practical consequence unless you are planning passages greater than miles in length. Gnomobic Content Related Overviews Mercator projection.
Photocopiers often tend to change the original scale. Conic Equirectangular Sinusoidal Two-point Werner. In order to draw a great circle on a Mercator chart—the projection being a relatively complex curve always concave to the equator—the route is first drawn on a gnomonic chart by connecting the plotted positions of the places of departure and destination with a straight line.
Gnomonic projection
Although it was generally believed that Godfray was the original inventor of this method of great circle sailing, it is interesting to note that a fhart explanation of the construction of a polar gnomonic chart, with a detailed example of a great circle route from the Lizard to the Bermudas, appeared in Samuel Sturmey’s Mariners’ Mirror, of For a Gnomonic Projection, imagine placing a screen tangential to the Earth’s surface and then project the features onto it obviously this is done mathematically.
More Like This Show all results sharing this subject: This page was last edited on 7 Juneat Because of the overlap of the existing charts, this problem is reduced to choosing the most appropriate map. The map distance from that point is a function r d of the true distance dgiven by.
You may skip to this section if you are not interested in these details now. The path of the shadow-tip or light-spot in a nodus-based sundial traces out the same hyperbolae formed by parallels on a gnomonic map. Figure 1 shows two gnomonlc and their great circles on the celestial sphere. Therefore always use the originals whenever you are going to make copies, otherwise you may add to the errors.
The reference lines are the inner ones, not the thick lines. Medicine and health Music Names studies Performing arts Philosophy.
Gnomonic chart - Oxford Reference
This is achieved by casting surface points of the sphere onto a tangent plane, each landing where a ray from the center of the sphere passes through the point on the surface and then on to the plane. Show Summary Details Overview gnomonic chart. Commons category link from Wikidata. That is the effect of Mercator projection. Therefore, use the originals you bought whenever you are going to make copies.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. From O all stars on the sphere are projected onto the plane of the map. The origin of the X, Y coordinates is located in the bottom left corner of the chrt X-axis to the right, Y-axis upwards.
Positions of a series of points on this line are taken from the gnomonic chart and marked on the Mercator chart.
